Image credit: Unsplash
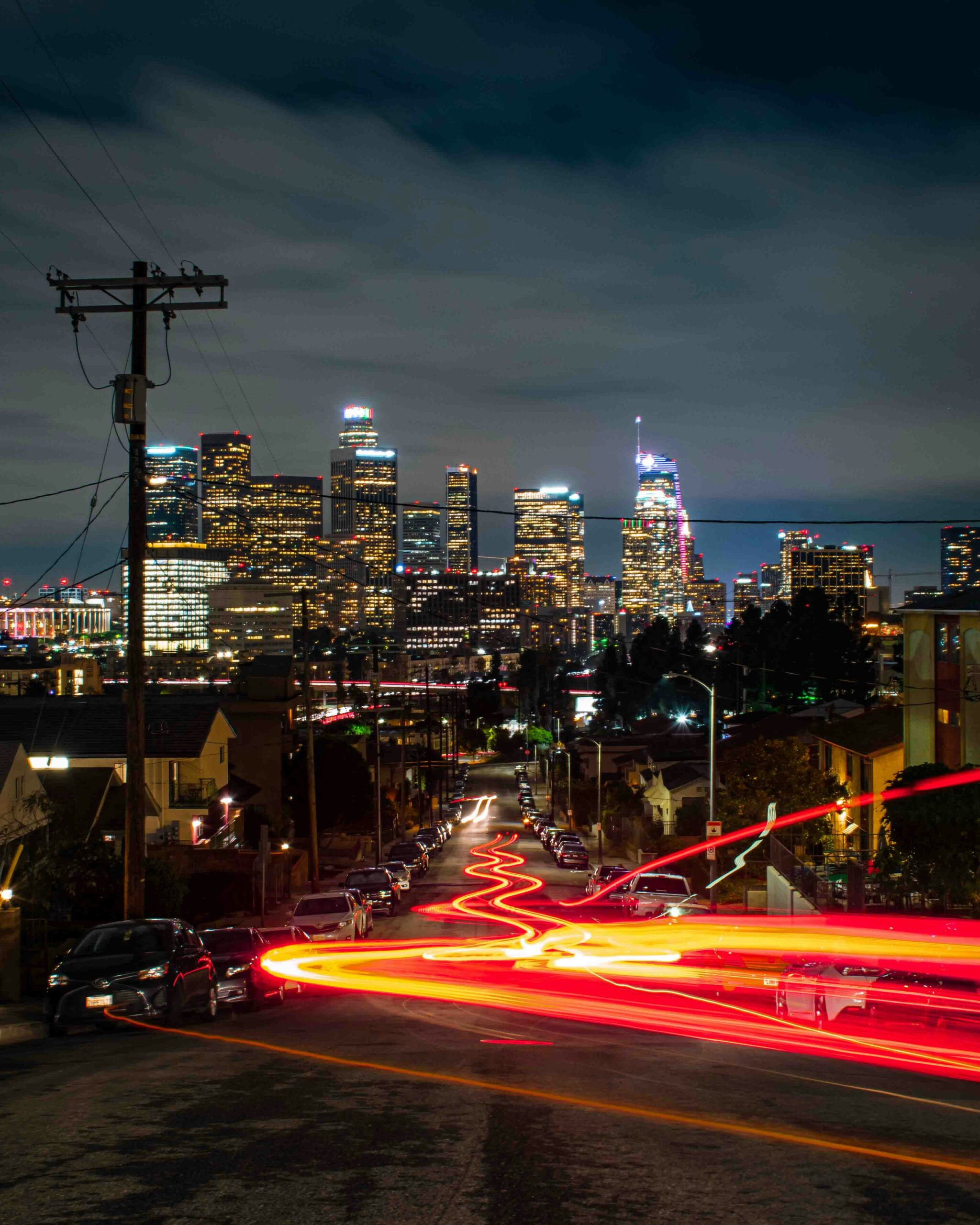
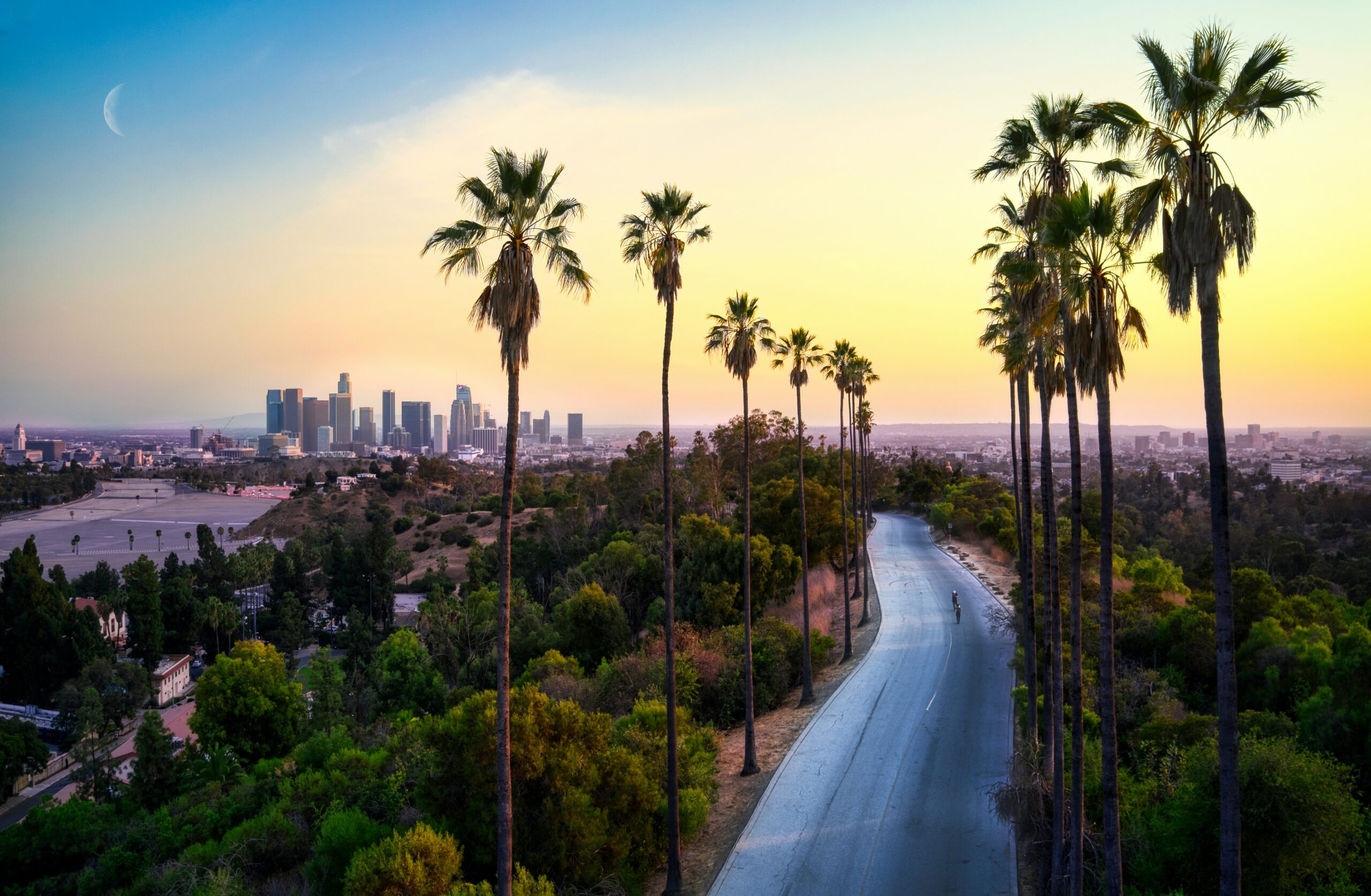
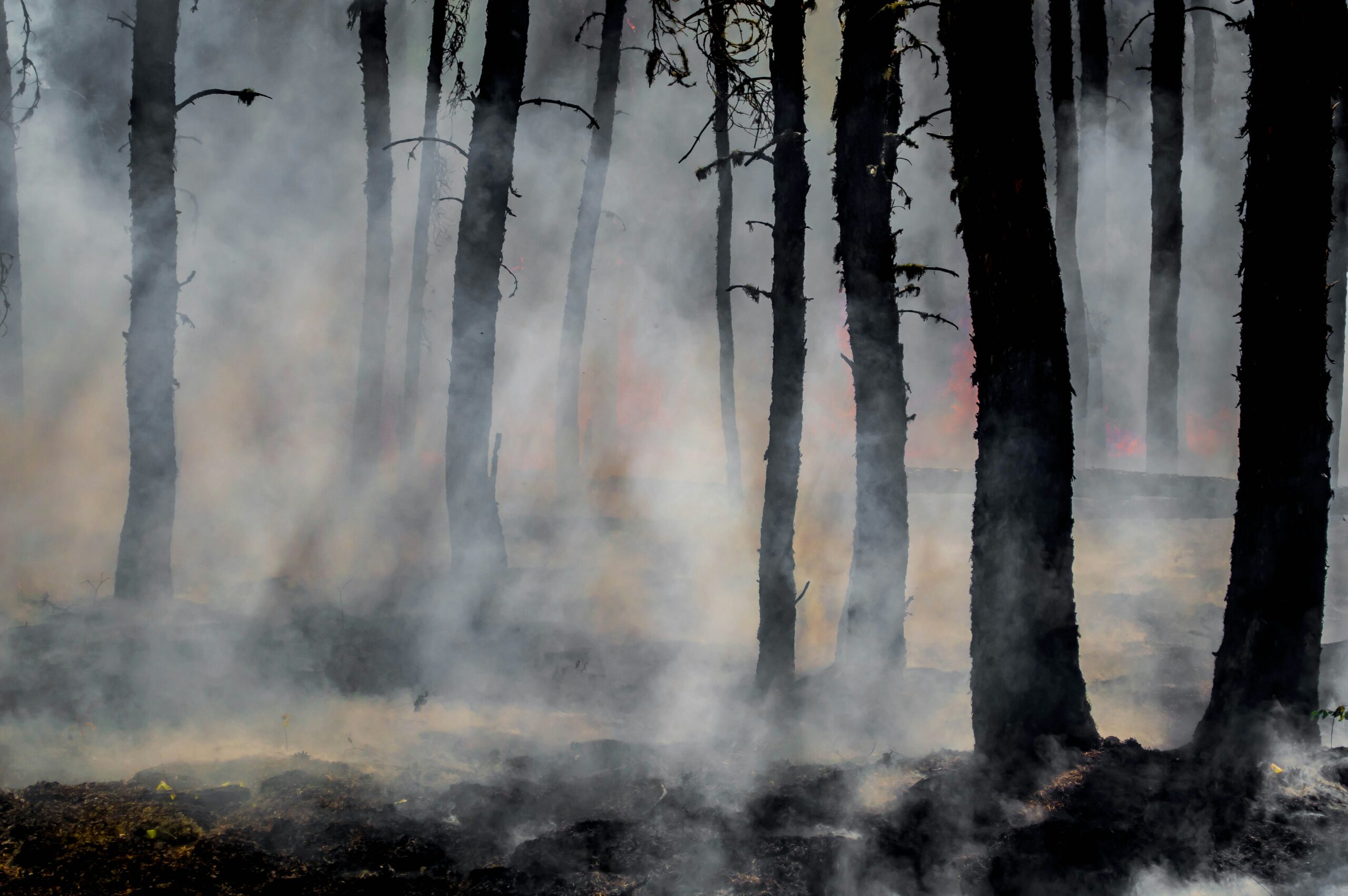
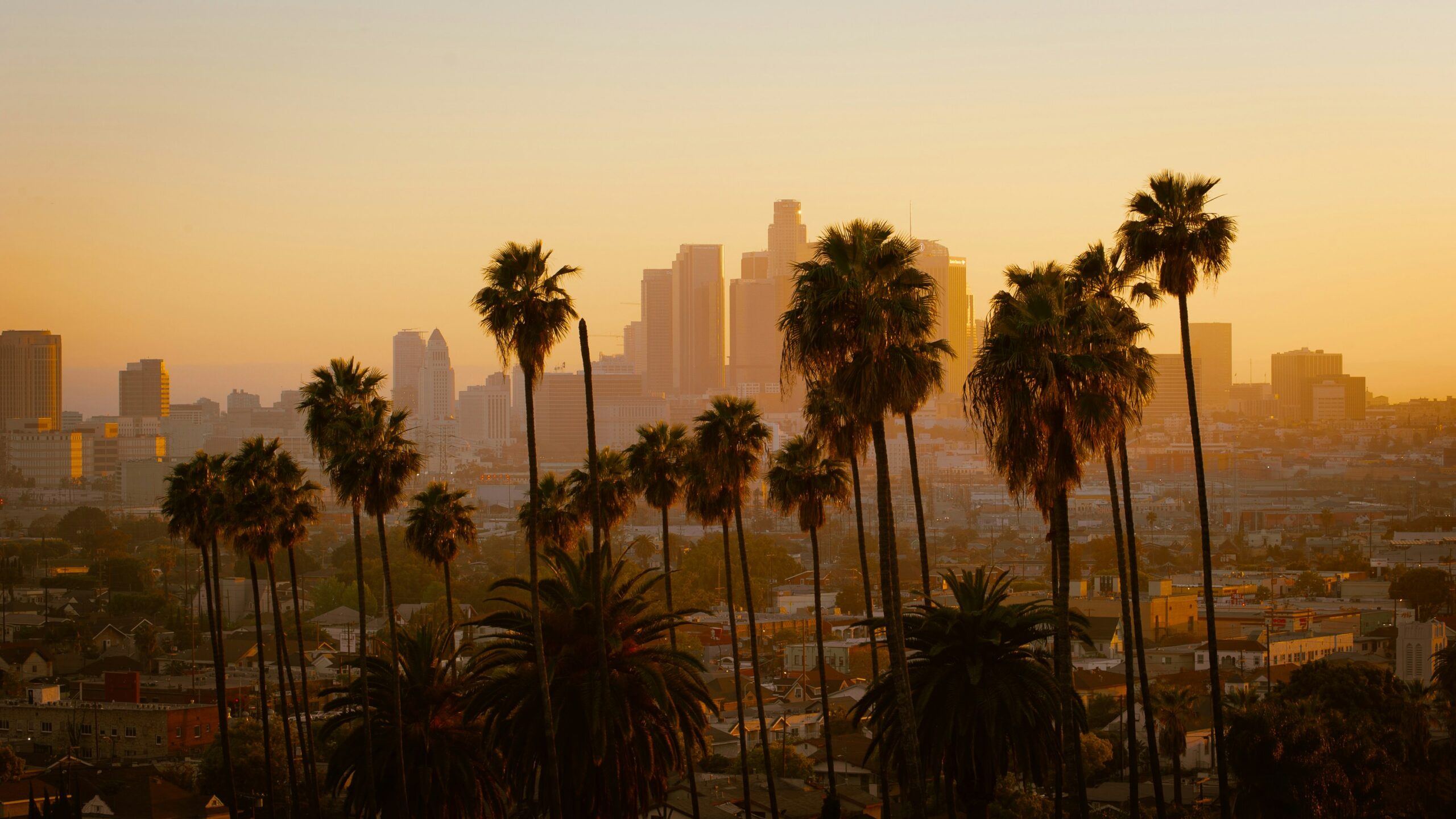
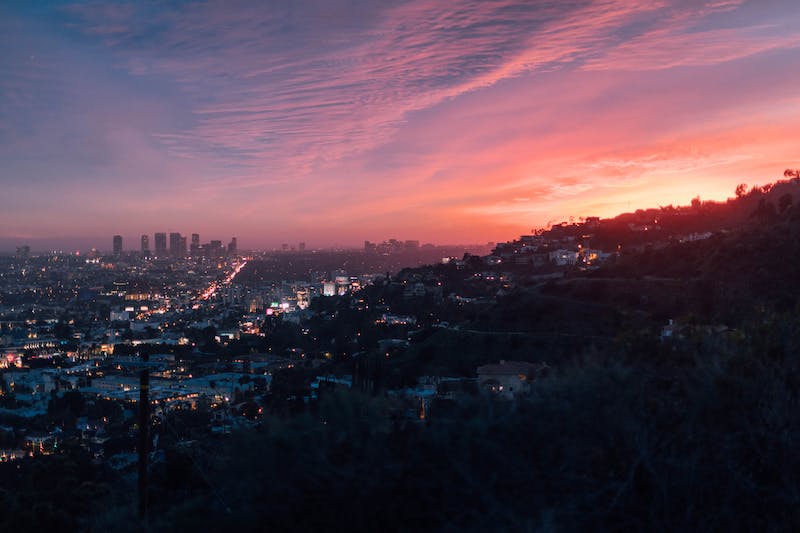
Last week, Greater Los Angeles was issued a sweeping air quality alert. L.A.’s unique geography and persistent pollution sources created challenging air conditions through this past Friday at midnight. Announced last Wednesday, the alert comes as the basin’s natural bowl-like terrain traps pollutants in a stagnant air mass across many areas.
Sprawling from the coast to the valleys, the poor air conditions impacted the following regions: Catalina and Santa Barbara Islands, the Santa Clarita Valley, Malibu Coast, Los Angeles proper, Palos Verdes Hills, the Western and Eastern Santa Monica Mountains Recreational areas, and the communities of Calabasas and Agoura Hills.
Dangers in the Air
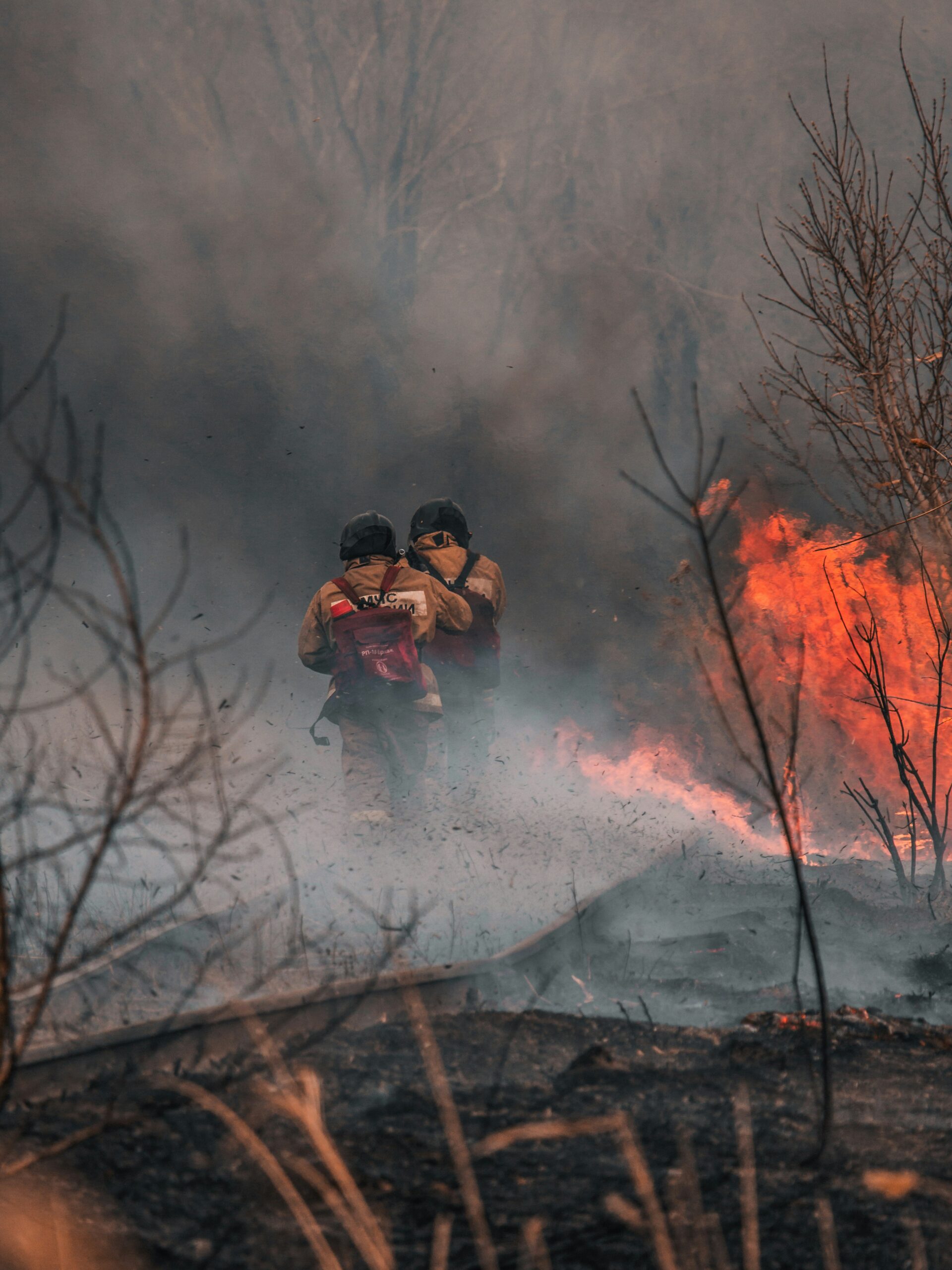
California endures some of the poorest air quality issues throughout the nation, mostly due to its high population density, high temperatures, frequent wildfires, and high human-caused emissions.
The terrible air quality in the Greater Los Angeles area is especially concerning given L.A.’s position in the American Lung Association’s 2024 State of the Air Report. This report ranked the Los Angeles-long Beach area among some of the country’s highest in ozone pollution. Ongoing emissions are a contributing factor to the region’s challenges; emission sources include vehicle exhaust, industrial activities, and port operations. Coupled with temperature inversions that prevent pollutant dispersion, the area is more prone to poorer air conditions.
“Particles in smoke can get deep into the lungs and cause health problems, including asthma attacks, increases in emergency room visits, and hospitalizations,” warned the National Weather Service Los Angeles/Oxnard, CA, which emphasized the air quality concerns were based on pollution levels forecasted for entire 24-hour periods.
Steps You Can Take
With L.A. being prone to terrible air conditions, health officials recommend several precautionary steps you can take during such periods. These include:
- Staying inside if possible, especially if you have respiratory issues, are elderly, or are a child.
- Limiting your outdoor activities to essential tasks only when necessary.
- Reduce the use of pollution-generating equipment, such as cars and gas-powered lawnmowers.
- Keep windows and doors closed.
- Running air conditioners and air purifiers when possible.
- Avoid using devices that bring in outside air, such as swamp coolers or whole-house fans, if alternative cooling methods are available.
State Measures to Address Air Quality Issues
California has implemented several measures that address air quality issues, including introducing strict vehicle emissions standards and promoting clean energy alternatives. Last month, regulators approved changes to the low carbon fuel standard, which now requires gas stations to provide a more expensive but cleaner fuel blend.
While a persistent concern for California, more air quality alerts have been issued this year than during 2023. These alerts can be accompanied by varying calls to action depending on the specific concern. Some residents have been advised to avoid refueling their cars, being asked to avoid driving their cars, or to find carpool options instead.
Air quality alerts are more common in the summertime because of the impact that hotter weather has on the formation of ground-level ozone, which is a harmful pollutant.
Also part of Wednesday’s alert was the banning of residential wood burning, which included the non-desert portions of Los Angeles, Riverside, and San Bernardino counties, as well as all of Orange County, according to the National Weather Service. Residents in these areas were reminded that burning wood in their fireplaces or any indoor/outdoor areas is prohibited, as well as burning manufactured fire logs, like those made from wax or paper. Exceptions to this alert included mountain communities above 3,000 feet, the Coachella Valley and the high desert, homes that rely on wood burning for heat, low-income households, and those without natural gas service.